What Causes a Boiler to Explode?
Importance of Boilers in Industrial and Residential Scenarios
Boilers play a key role in both industrial and civil scenarios. On the industrial side, it is widely used in major industries such as paper, chemical, food, etc., mainly for process heating, electrical or mechanical power production, and space heating. And steam boilers, the most common type of boiler, play a central role in all types of applications. In the residential sector, boilers provide warmth to homes and ensure people's comfort during the cold season.
A boiler explosion is an extremely serious disaster that can cause severe property damage, destroy factory facilities, residential homes, and more. More frighteningly, it can lead to injuries and deaths, bringing grief to countless families. Understanding the causes of boiler explosions is crucial to preventing such tragedies from occurring. Next, we will delve into what triggers a boiler explosion.
How Boilers Work
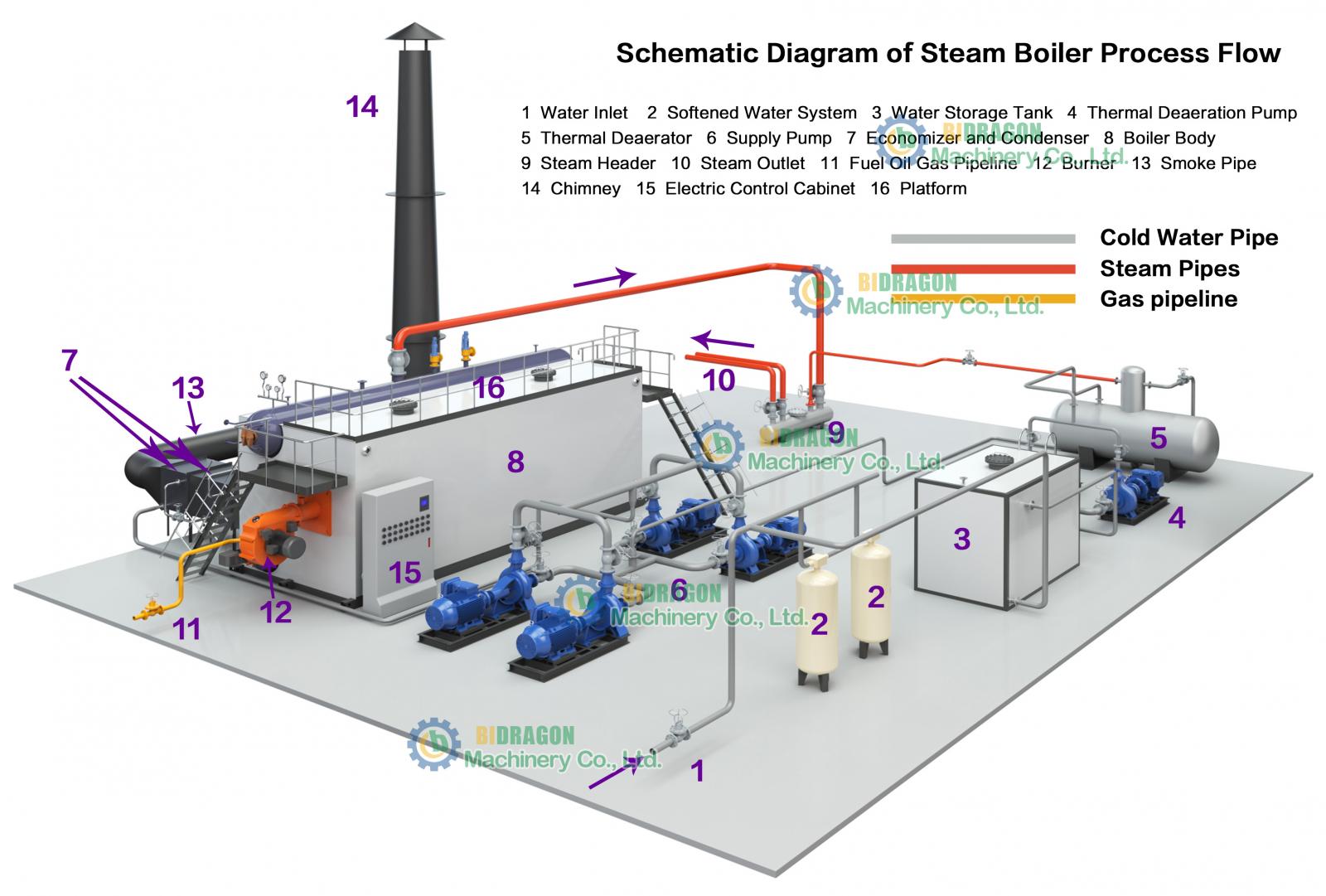
Basic workflow step-by-step analysis
Set Temperature:The user sets the thermostat in their home or business to the desired temperature level based on demand.
Start Signal:When the thermostat detects that the ambient temperature has dropped below the set point, it sends a start command to the boiler.
Energy Conversion:When the boiler is activated, it utilizes an energy source such as natural gas, electricity or fuel oil to generate heat.
Heating Water:The heat generated by the combustion of the fuel is transferred to the water inside the boiler to warm the water.
Heat Transfer:The heated water or steam produced is passed through radiators or radiant floor systems, which distribute the heat into the room and warm the air.
Recirculation Return: As the heat is dissipated, the water gradually cools and the steam condenses into water and they flow back into the boiler, waiting to be heated again.
Stopping operation: When the room temperature reaches the set point, the thermostat notifies the boiler to stop.
Pressure plays an important role in boiler operation. Normally, the pressure inside the boiler rises significantly. And when the pressure exceeds the tolerance limit that the boiler is designed to withstand, it can lead to hazards, the most serious of which is an explosion. Therefore, understanding the pressure changes and controlling the pressure within the safe range is a key link to ensure the safe operation of the boiler.
The causes of boiler explosion
Overpressure
Overpressure explosion principle: when the internal pressure of the boiler is too high, beyond the range it is designed to withstand, the structural integrity of the boiler will be damaged. This excessive accumulation of pressure may eventually lead to boiler rupture, triggering an explosion.
Common Causes of Overpressure: A malfunctioning pressure relief valve is one of the common factors leading to overpressure, and when it fails to release steam properly, the pressure will continue to rise. In addition, improper boiler operation, such as incorrect settings or prolonged operation without proper monitoring, can also cause a dangerous buildup of pressure.
Pressure Monitoring and Maintenance Essentials: In order to prevent malfunctions caused by overpressure, it is vital that pressure is monitored and maintained on a regular basis. Manometers should be properly calibrated to ensure accurate readings. Also, the pressure relief valve should be checked regularly to ensure that it opens properly to release excess pressure in the event of overpressurization.
Corrosion
Corrosion is the mechanism of damage to the boiler structure: when exposed to high temperatures and humidity for a long period of time, the metal parts of the boiler will gradually be corroded. This corrosion reduces the strength of the metal and creates weak points in the boiler structure. Over time, these weak points can trigger sudden failures and even lead to explosions.
Anti-corrosion measures: In order to prevent corrosion, the boiler needs to be inspected on a regular basis to detect any signs of corrosion such as rust spots or dents. In addition, corrosion inhibitors can be added to the water to slow down the chemical reaction between the metal and the water, thus reducing the rate of corrosion.
Poor water quality
Impurities in the water: If the water used in the boiler contains impurities such as minerals and salts, these impurities will gradually accumulate over time and form scale. The presence of scale can lead to uneven heating of the boiler, reducing thermal efficiency and potentially triggering localized overheating. In severe cases, scale buildup can block water flow paths, leading to high water temperatures, a sharp rise in steam pressure, and ultimately an explosion.
Importance of water quality treatment and filtration: Installing a water quality treatment system is an effective way to remove impurities from the water, through which the water source can be purified to reduce impurities from entering the boiler. At the same time, regular testing of water quality to ensure that it meets the requirements of boiler operation, can effectively reduce the risks caused by water quality problems.
Operational errors
Human error factor: operational error is an important cause of boiler explosion. For example, improper maintenance of the boiler, long-term neglect of cleaning or maintenance work; operating process errors, such as starting or shutting down the boiler in the incorrect order; the boiler sends out abnormal signals, such as abnormal noise or pressure fluctuations, etc., turn a blind eye.
The need for operator training: Comprehensive training for operators is essential. The training should cover the correct operation methods, daily maintenance points and safety precautions. And retraining should be organized on a regular basis so that operators are always up-to-date with the latest operating specifications and safety knowledge.
Low water level
Importance of maintaining a normal water level: During boiler operation, water plays an important role as an insulator, protecting the metal walls of the boiler from high temperature erosion. When the water level is too low, the metal structure will be directly exposed to high temperatures, which may lead to melting, deformation, cracking or loosening of the metal, which in turn will trigger water leakage. In this case, the boiler is highly susceptible to explosion.
Causes of low water level: The low water level may be due to the malfunctioning of the feed pump or water level control device, which is unable to supply water to the boiler properly. In addition, insufficient water in the feedwater tank and lack of effective supervision and management may cause the boiler water level to be too low.
Measures to maintain the water level: install monitoring equipment such as water level sensors and automatic water cutoff systems that can monitor water level changes in real time. At the same time, key components such as pumps, valves and water level sensors should be maintained on a regular basis to ensure their normal operation.
Overheating
Definition of overheating: Overheating is a condition in which the internal temperature of the boiler exceeds the safe limit.
Common causes of overheating: In power plants and cogeneration plants, localized flue gas flow deviations in the superheater can cause part of the tube bundle to overheat and become too hot, with a risk of explosion. Deposits such as scale in the tubes impede heat transfer, resulting in higher tube wall temperatures. Improper combustion control in the combustion chamber can also cause the tubes to overheat. In addition, when the boiler is seriously short of water, some of the steam generating tubes overheat or dry out, at which time the water is refilled and the tubes are damaged due to thermal stress and may even explode.
Methods to prevent overheating: Ensure the quality of feedwater and boiler water to reduce corrosion and fouling in the piping. Avoid water circulation problems and prevent the boiler from running at low load for long periods of time. Prevent damage to external piping and optimize the combustion process in the combustion chamber.
Calculation errors
Principle of explosion triggered by calculation error: In the design process of boiler, inaccurate calculation of its size, capacity or pressure-bearing capacity may lead to overheating or uncontrolled pressure when the boiler is in operation. In addition, the selection of unsuitable fuel, which produces heat beyond the thermal capacity of the boiler, can also trigger overheating and explosion risk. At the same time, inaccurate input of data when calculating parameters such as pressure, temperature or volume can lead to incorrect calculations of boiler performance and pressure, which can pose an explosion risk.
Measures to prevent calculation errors: Provide regular safety training to employees involved in boiler operation and maintenance to improve their accuracy in relevant calculations. Risks can be minimized by working with an energy sales or operation service company to ensure the accuracy of calculations with the help of a professional. For older boilers, where there are inaccurate calculations or safety standards are not met, replacement with new equipment should be considered.
Signs of a possible boiler explosion
Abnormal noise
A normally operating boiler has a smooth sound. If you hear abnormal sounds such as banging, whistling or popping from the boiler, you need to pay attention. These sounds could mean that pressure is building up inside the boiler or that there is an air blockage problem in the system.
Leaks and drips
Noticing areas of standing water or moisture around the boiler is a red flag that there may be a leak in the internal components of the boiler. Leaks can affect the pressure inside the boiler, triggering a potential safety hazard.
Sudden drop in pressure
Always keep an eye on your boiler's pressure gauge; if the pressure suddenly drops, this could suggest a faulty pressure relief valve or other critical component. Low pressure can cause the boiler to overheat and, in extreme cases, can also trigger a boiler failure.
Strange odors
If you smell a strange odor, especially one that resembles natural gas, it should not be ignored. A gas leak is an extremely dangerous situation and should be dealt with by contacting a professional as soon as it is detected.
Age of the boiler
Like any other appliance, boilers have a useful life. If a boiler is approaching or has exceeded its expected lifespan, the likelihood of problems increases. Regular maintenance is especially important for the smooth operation of this type of boiler.
Measures to prevent boiler explosions
Design preventive measures
When designing a boiler, it is vital to use a rational structure. Reasonable design can ensure that the boiler withstands pressure and temperature changes during operation, and reduce safety hazards caused by unreasonable structure.
Measures related to installation, maintenance and renovation
Strengthen the welding management: when installing, repairing and remodeling the boiler, the welding quality should be strictly controlled. Ensure that the welding process meets the standards and avoid welding defects, as welding problems may affect the overall strength of the boiler.
Follow the specification for heat treatment and flaw detection: in accordance with the requirements of the relevant specifications, heat treatment is carried out on the welded parts to eliminate welding stress. At the same time, carry out flaw detection testing to detect potential internal defects in time to ensure the safety of the boiler.
Material management
Selecting suitable materials is the basis for ensuring boiler safety. Defective materials, as well as wrong steel and welding materials, should be avoided. High-quality materials can improve the durability and safety of the boiler.
Utilization Management
Avoid operating errors: operators should operate in strict accordance with the operating procedures to avoid accidents caused by improper operation. For example, the operating parameters of the boiler should be set correctly to avoid over-temperature, over-pressure and overload operation.
Regular inspection and maintenance: the boiler should be inspected regularly to find and solve problems in time. At the same time, make sure that the safety devices, such as pressure release valve and water level control device, can work properly.
Inspection
Regular and comprehensive inspections are essential to boiler safety. Through inspection, defects in the boiler, such as corrosion, cracks, etc., can be found in time and effective repair measures can be taken to prevent the problem from deteriorating and causing an explosion.
Specific preventive measures for different types of boiler hazards
Preventive measures for boiler tail re-ignition
Reduce incomplete combustion losses: minimize the incomplete combustion phenomenon in the combustion process and reduce the accumulation of combustibles in the tail. At the same time, reduce the number of starts and stops of the boiler, as frequent starts and stops may increase the risk of re-ignition.0
Enhance soot blowing and sealing of the tail heating surface: Blow soot on the tail heating surface on a regular basis to remove the accumulated soot and prevent re-ignition of the combustible materials in the accumulated soot. In addition, make sure that the flue holes and flue baffles are well sealed to avoid air leakage to trigger re-ignition.
Preventive measures for boiler furnace explosion
Installation of reliable furnace safety protection devices: According to the capacity and size of the boiler, install appropriate and reliable furnace safety protection devices, such as flame monitors, flame failure protection devices, etc., which can monitor the combustion situation in the furnace in a timely manner, and take measures quickly in the event of an abnormality.
Improve the blast resistance of the furnace chamber and rigid beam: optimize the design of the furnace chamber structure to enhance its blast resistance. At the same time, strengthen the strength of the rigid beam, so that it can maintain structural stability in the furnace chamber when the pressure changes suddenly.
Strengthen the use of management and stoker technical level: standardize the operation process of the stoker, strengthen their training, improve their technical level and emergency response capabilities, to ensure that the furnace can respond correctly in the event of anomalies.
Preventive measures for water shortage in boiler steam bag
Water shortage accident treatment: When there is a slight water shortage, water can be replenished to the boiler immediately to restore the water level to normal. However, if it is a serious water shortage, the furnace must be stopped in an emergency, it is strictly prohibited to replenish water to the boiler at this time, so as not to cause more serious accidents.
Full water accident treatment: Once the water accident occurs, should immediately close the water valve, stop the water supply to the boiler. At the same time, start the recirculation pipe of the coal economizer, reduce combustion, open the discharge valve and the superheater and steam piping on the trap. When the water level returns to normal, close the discharge valve and each trap. After carefully checking and eliminating the cause of the accident, normal operation can be resumed.
General Principles of Accident Handling
Operator's responsibility
Operators should operate immediately in accordance with the prescribed handling measures when an accident occurs, solve the problem quickly and prevent further expansion of the accident. Their timely action is essential to minimize losses.
Determine the cause of the accident
Accurately identifying the cause of an accident is the key to developing the best, fastest and least damaging solution for the system. Only when the cause is clearly identified can targeted measures be taken to prevent similar accidents from recurring.
Immediate action
When signs of abnormality (i.e. accident symptoms) appear in the equipment, the operator must take immediate action or activate the appropriate emergency plan to prevent the accident from nipping in the bud and developing into a serious disaster.
Operator's Knowledge Base
Boiler operators should have a thorough understanding of the boiler system and the accident handling process so that they can react quickly when an accident occurs, accurately determine the problem and repair it.
Accident Reporting
After an accident occurs, it should be reported to other relevant departments in a timely manner so that all parties can work together to develop a long-term solution to completely eliminate the safety hazard and prevent the accident from happening again.
How to promote boiler safety
Training
Actively participating in boiler safety training to learn the proper operation methods, maintenance points, and emergency response knowledge of the boiler can effectively improve the operator's safety awareness and skill level.
Follow the manufacturer's instructions
Strictly following the operating manual and maintenance instructions provided by the boiler manufacturer can ensure that the boiler operates within its design parameters and reduce safety risks caused by improper operation.
Regular Inspections
Regular comprehensive inspections of the boiler, including exterior inspections, internal structure inspections, safety device inspections, etc., to detect potential problems and repair them in a timely manner, are an important means of ensuring the safe operation of the boiler.
Reporting of safety hazards
If you find any potential safety hazards in the boiler, such as damaged parts, abnormal sound, strange odor, etc., you should report them to your superiors or notify the relevant professionals to deal with them in a timely manner, and don't ignore any signs that may lead to accidents.
Keep the boiler area clean
Keep the area around the boiler clean and tidy with no accumulation of debris, which not only facilitates the work of the operator but also reduces other safety risks such as fire.
Avoid overloading
Don't allow the boiler to run at more than its designed load; overloading can cause the boiler to become pressurized and overheated, increasing the risk of an explosion.
Ensure good ventilation
During boiler operation, make sure the surrounding area is well ventilated, especially for boilers using gas or oil. Good ventilation prevents combustible gases from building up and reduces the risk of explosion.
Keep away from flammable materials
Place the boiler away from flammable materials to avoid fire caused by boiler leakage or overheating, which can further lead to an explosion.
Conclusion
Boiler explosions are mainly caused by overpressure, corrosion, poor water quality, operational errors water level is too low overheating and calculation errors. These factors are interrelated, and problems in any one of them may lead to serious consequences.
The risk of boiler explosion can be significantly reduced by implementing the preventive measures mentioned above, such as proper design and operation, regular maintenance of water quality treatment, etc., as well as actively promoting boiler safety. Prevention is better than cure, only the implementation of safety to every detail, in order to ensure the safe operation of the boiler.
I hope that readers can pay attention to boiler safety issues, and effectively follow the relevant requirements and recommendations for the correct operation and maintenance and management of the boiler. Starting from ourselves, we will contribute to the safety of people's lives and property and the normal operation of production and life.