The Types of Steam Boilers
Steam boilers play an extremely important role in many industries. From power supply in industrial production, to heating in commercial buildings, to generating electricity in power stations, the steam boiler plays an indispensable role. Its development has witnessed the advancement of human technology, from a simple device similar to a kettle heated over a fire, to a modern, complex and efficient system. During this evolution, the types of steam boilers have also become diverse. So what are the different types of steam boilers? What are their characteristics and application scenarios? Let's take a closer look.
What is a steam boiler?

A steam boiler is a system that generates steam by heating water, functioning as a heat exchanger that converts water into steam for external applications. It consists of two main components: a combustion chamber and a water vessel. Steam boilers span a wide range of sizes, from small units to larger ones capable of handling more arduous tasks.
Steam boilers heat water by burning fuel to produce steam, a process that involves three forms of heat transfer: radiation, convection, and conduction. Radiation is the direct transfer of heat in the form of electromagnetic waves from a hot object to a cold object; convection relies on the flow of a fluid (liquid or gas) to transfer heat; and conduction transfers heat through the vibration of molecules within an object.
Types of Steam Boilers
Categorized by boiler structure
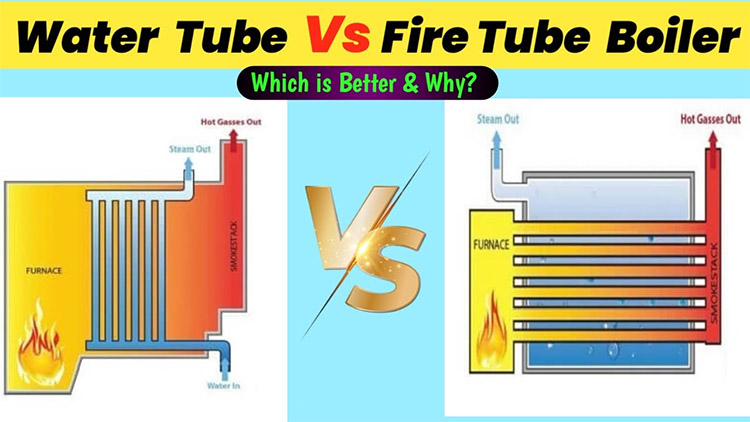
Fire Tube Boiler
In a fire-tube boiler, the combustion chamber is connected to the boiler cylinder, and the gas transfers heat to the water supply through the fire tube. In a fire tube boiler, the high temperature gas produced by combustion flows inside the fire tube, and the heat is transferred to the water outside the tube through the wall of the fire tube, causing the water to be heated and evaporate to produce steam.
The advantages of fire tube boilers are simple structure, easy operation, relatively low cost, and relatively low requirements for water quality. However, its disadvantages are relatively low thermal efficiency, limited steam production, and due to the large diameter of the pot shell, the ability to withstand pressure is limited.
Fire tube boilers are commonly used in small industrial production, hotels, schools and other places to provide hot water or a small amount of steam, such as small food processing plants to provide steam for food processing, for the hotel's laundry room to provide steam for ironing clothes and so on.
Water tube boiler
The combustion chamber of a water tube boiler is separate from the cylinder and the flue gas transfers heat to the water supply through water tubes. In a water tube boiler, the water flows inside the water tube and the flue gas flushes outside the water tube. Heat is transferred from the flue gas to the water inside the water tube, vaporizing the water to produce steam.
Compared with fire tube boilers, water tube boilers have higher thermal efficiency, can produce steam at higher pressures and temperatures, and are safer due to the smaller diameter of the water tubes and their greater pressure-bearing capacity. The disadvantage is that the structure is relatively complex, the water quality requirements are higher, maintenance and operation requires more specialized technicians.
Water tube boilers are commonly used in large-scale industrial production, power stations and other occasions with high requirements for steam volume and steam parameters. For example, in large-scale chemical enterprises, a large amount of high-temperature and high-pressure steam is needed to carry out chemical reactions; in power stations, the high-temperature and high-pressure steam produced by water-tube boilers is used to drive the turbine to generate electricity.
Shell and Tube Boiler
A shell-and-tube boiler consists of a combustion chamber, a boiler cylinder, and a flue gas tube shell, through which the flue gas transfers heat to the water supply. In a shell-and-tube boiler, high-temperature flue gases flow inside the tube shell, and the heat is transferred through the tube shell to the water outside the tube to produce steam.
Shell and tube boiler combines some features of fire tube boiler and water tube boiler with better heat transfer performance. It has applications in some specific industrial fields, such as in some industrial production that requires medium-sized steam supply, the shell and tube boiler can meet its requirements for steam quantity and steam quality.
Classification by boiler use
Industrial boilers
Industrial boilers are used to supply steam during industrial production and are widely used in many industries such as chemical, textile, and food processing. In the chemical industry, steam can be used for chemical reaction heating, material evaporation and distillation, etc.; in the textile industry, steam is used for fabric dyeing, drying and shaping processes; in the food processing industry, steam is used for cooking, sterilization and drying of food.
Industrial boilers usually need to have high steam production and stable steam parameters to meet the needs of different industrial production processes. Different industries also have some special requirements for industrial boilers, for example, the chemical industry may require boilers to be able to adapt to special process conditions, while the food processing industry has strict requirements for the hygiene standards of boilers.
Power generation boiler
A power generation boiler is a steam generating device used in a power station to produce high temperature and high pressure steam to drive a turbine to generate electricity. In a power station, fuel is burned in the boiler to release a large amount of heat, which heats water into high-temperature, high-pressure steam, which drives the turbine to rotate, which in turn drives the generator to produce electricity.
With the continuous progress of science and technology, power generation boilers have made many technological breakthroughs in improving thermal efficiency and reducing pollutant emissions. For example, the adoption of advanced combustion technology and waste heat recovery systems has improved energy utilization; and the installation of highly efficient desulphurization, denitrification and dust removal equipment has reduced pollution of the environment.
HVAC boiler
HVAC (heating, ventilation and air conditioning) boilers are mainly used to provide hot water or steam for heating systems. In winter, the hot water or steam produced by the boiler is piped to radiators in the building to provide warmth inside. HVAC boilers play a vital role in heating some of the largest commercial buildings, office buildings and residential neighborhoods.
When selecting an HVAC boiler, factors such as the size of the building, insulation, and heat load requirements need to be taken into account to ensure that the size and efficiency of the boiler meets the heating needs of the building, while realizing energy efficiency and comfortable heating.
Classification by boiler operating pressure
Low-pressure boilers (working pressure <1.6MPa)
Low-pressure boilers are suitable for application scenarios that do not require high steam pressure, such as small laundries and small printing and dyeing plants. These places utilize low pressure steam for simple heating, ironing or processing operations.
Low pressure boilers have the advantages of lower cost, simple structure, easy operation and maintenance. Due to its low working pressure, the requirements for equipment materials and manufacturing process are relatively low, so the investment cost is relatively small.
Medium pressure boiler (1.6 - 4.0MPa)
Medium-pressure boilers are mainly used in industrial fields that require medium-pressure steam, such as certain chemical production processes and small cogeneration plants. On these occasions, medium pressure steam is able to meet specific process requirements, for example, in some chemical synthesis reactions, steam at a certain pressure is required to provide the heat and pressure conditions needed for the reaction.
Medium-pressure boilers find a balance between pressure requirements and system complexity to meet certain industrial production needs without making equipment and operations too complex and costly.
High pressure boilers (4.0 - 9.8MPa)
High-pressure boilers are commonly used in industrial production processes that require high steam pressure and temperature, such as high-temperature and high-pressure reactions in large chemical companies and power generation processes in large cogeneration plants. In these industries, high-pressure steam can provide higher energy to meet the demands of complex processes and large-scale power generation.
However, high-pressure boilers face many challenges in their design and operation. Due to the high operating pressure, the boiler is subject to extremely high requirements for material strength, sealing performance and safety protection measures. Meanwhile, the operation and maintenance of high-pressure boilers require specialized technicians and strict operating procedures to ensure their safe and stable operation.
Ultra-high-pressure boiler (working pressure>9.8MPa)
Ultra-high-pressure boilers are mainly used in some specialized fields, such as advanced thermal power stations and certain high-end chemical production. In ultra-supercritical thermal power generation technology, ultra-high-pressure boilers are able to produce steam with higher parameters, greatly improving power generation efficiency and reducing energy consumption and pollutant emissions.
In order to meet the requirements of ultra-high-pressure operation, the ultra-high-pressure boiler adopts advanced scientific and technological achievements in material research and development, manufacturing process and control technology. For example, special steel materials that are resistant to high temperature and pressure are used, and precision machining processes and intelligent control systems are employed to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the boiler under extreme conditions.
Classification by boiler fuel
Coal fired boilers
Coal-fired boilers use coal as fuel. Coal combustion releases a large amount of heat, which is used to heat the water in the boiler to produce steam. Coal-fired boilers have the advantage of high thermal efficiency and are especially suitable for regions with abundant coal resources and relatively low prices. Coal-fired boilers have been widely used in some large-scale industrial enterprises and thermal power plants to meet large-scale demand for steam and electricity.
However, coal-fired boilers also have obvious environmental problems. Coal combustion produces a large number of pollutants, such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, etc., which cause serious pollution to the atmospheric environment. With increasingly stringent environmental requirements, many regions have restricted the use of coal-fired boilers or required them to undergo environmental retrofits.
Oil fired boilers
Oil fired boilers use petroleum or heavy oil as fuel. The fuel oil is burned in the boiler to convert chemical energy into heat, which in turn heats water to produce steam. The advantages of an oil-fired boiler are higher combustion efficiency and quick startup to quickly meet changes in steam demand. Oil-fired boilers produce relatively fewer pollutants than coal-fired boilers, but still emit some amount of pollutants such as nitrogen oxides and particulate matter.
Oil fired boilers are suitable for places that require a high speed of steam supply and a convenient fuel supply. For example, on some ships, where space is limited and a quick-start power source is needed, an oil-fired boiler is a common choice. In addition, oil-fired boilers may be used in remote areas where coal is not readily available and fuel oil is relatively easy to supply.
Gas boilers
Gas boilers use natural gas or LPG as fuel. Natural gas or LPG is mixed with air in the boiler and burned, releasing heat to heat water to produce steam. Gas boilers have the significant advantage of good environmental performance. Compared with coal-fired and oil-fired boilers, the emission of pollutants in the combustion products is greatly reduced, especially the emission of sulfur dioxide and particulate matter is extremely low, which meets the modern environmental protection requirements.
At the same time, the gas boiler is easy to operate, high degree of automation, according to the steam demand to automatically adjust the amount of combustion, has a high thermal efficiency. Therefore, gas boilers are popular in small to medium-sized industrial and civil fields, such as in some small factories, hotels, schools and residential neighborhoods, often used for heating and providing domestic hot water.
Biomass boiler
Biomass boilers are fueled by biomass materials such as biomass pellets and straw. The biomass fuel is burned in the boiler to generate heat, which is used to heat water to produce steam. Biomass boilers are characterized by the use of renewable energy, and their fuel is derived from biomass, which is a renewable resource that reduces dependence on fossil energy and is conducive to the realization of sustainable development.
In addition, carbon dioxide emissions from biomass fuel combustion are basically balanced with the amount of carbon dioxide absorbed during the growth of biomass, which has a small impact on carbon emissions on the environment from the perspective of the entire life cycle. However, biomass boilers also face a number of challenges in practical application, such as the stability of biomass fuel supply, high fuel storage and handling requirements, and possible slagging during the combustion process, which need to be addressed with appropriate technical measures.
How do Steam Boilers Work?
Steam boilers generate pressurized steam power by heating water to the boiling point using a combustible fuel source. Specifically, the way the water is heated depends on whether it is a fire-tube or water-tube boiler, and the main difference between these two types of boilers is reflected in their names.
Operation of fire tube boilers
In a fire tube boiler, a combustible fuel source is located inside a tube surrounded by a vessel filled with water. As the fuel burns inside the tube, the tube gradually heats up the surrounding water, eventually producing steam. Think of it like a heating rod placed in a bucket of water, where the heat generated by the rod is transferred to the water in the bucket, causing the water to warm up and eventually boil to produce steam. In this process, heat is transferred from the burning fuel to the tube and from the tube to the surrounding water primarily by conduction and convection.
Operation of a water tube boiler
In a water tube boiler, the water is contained within multiple tubes, and the heat generated by the combustible fuel source is applied to the outside of the tubes to produce steam. This is akin to placing multiple straws over a fire, where the water inside the straws is heated by the external flame to produce steam. Unlike fire tube boilers, the transfer of heat from fuel to water in a water tube boiler relies primarily on radiation and convection. Because of this structural feature of water tube boilers, it has certain advantages in heat transfer efficiency and withstand pressure.
Which Steam Boiler Type is Best?
Choosing a steam boiler is not simply a matter of determining which type is best, but requires a combination of factors such as actual application scenarios, performance requirements, budget, and manufacturer's reputation.
Steam boiler types and their characteristics
There are a wide variety of steam boilers on the market today, with the common ones being coal-fired steam boilers, oil-fired steam boilers, gas-fired steam boilers, and electrically heated steam boilers. Coal-fired boilers with high thermal efficiency, suitable for large factories and other places with high demand for steam and convenient supply of coal; oil-fired boilers start quickly, high combustion efficiency; gas-fired boilers are environmentally friendly, easy to operate, widely used in small to medium-sized industrial and civil applications; electrically heated steam boilers are clean and non-polluting, with precise control, but with relatively high operating costs, and are often used in environmentally demanding and small steam dosage occasions. small occasions.
Performance and quality
When choosing a steam boiler, performance indicators are critical. Thermal efficiency has a direct impact on the efficiency of energy utilization, and an efficient boiler can produce more steam while consuming less fuel, thus reducing operating costs. Pressure stability is especially critical for some industrial production processes with strict requirements for steam pressure, and unstable pressure may affect product quality or even lead to production accidents. In addition, the boiler's material, manufacturing process, and heat exchanger design all have a significant impact on its performance.
Consideration of actual needs
Different scenarios have different needs for steam boilers. Industrial production usually requires a continuous and stable supply of steam to ensure the continuity of the production process. For example, in chemical production, steam is used as a reaction heat source or power source, once the supply is interrupted it may lead to the stagnation of the entire production process, resulting in huge economic losses. And in the food processing industry, there are higher requirements for boiler hygiene and safety due to the food safety issues involved. For example, the steam used in food processing must not contain substances that are harmful to the human body, so the boiler materials and water treatment system need to meet strict hygiene standards.
Cost and budget
Cost and budget are factors that should not be overlooked when purchasing a steam boiler. Different types of steam boilers and their configuration differences will lead to different prices. Generally speaking, the initial investment cost of coal-fired boilers is relatively low, but the fuel cost during operation and the investment cost of environmental protection equipment is high; the initial investment cost of gas-fired boilers may be higher, but the operating cost is relatively low, and the environmental performance is good, and the later maintenance cost is also low.
Conclusion
When choosing a steam boiler, you can not generalize which is the best, but to fully consider the performance, actual demand and cost and other factors. Only by comprehensively weighing these factors can you choose the steam boiler that best suits your needs. I hope that readers understand the content of this article, according to their own specific circumstances, further in-depth exploration and research, to choose the right steam boiler. If you need more detailed information, you can refer to the relevant industry standards and professional books, or consult us for professional technical guidance and thermal solutions.