How does an Industrial Boiler Work
Industrial boilers play a key role in many industries, and are at the heart of manufacturing plants, hospitals, and oil refineries. Their main function is to provide the necessary steam or hot water for various production processes. So how does an industrial boiler work? Next, let's take a step-by-step look.
What is an Industrial Boiler?
The core task of an industrial boiler is to convert water into steam by applying heat. Essentially, this device follows a simple but important principle: to realize the transfer of energy from fuel to water.
In this process, the energy contained in the fuel is released and transferred to the water inside the boiler, causing a change in its state.
Different Types of Industrial Boilers
There are many different types of industrial boilers, which can be categorized based on differences in design, operating pressure, and fuel type.
Here are four common types of steam boilers.
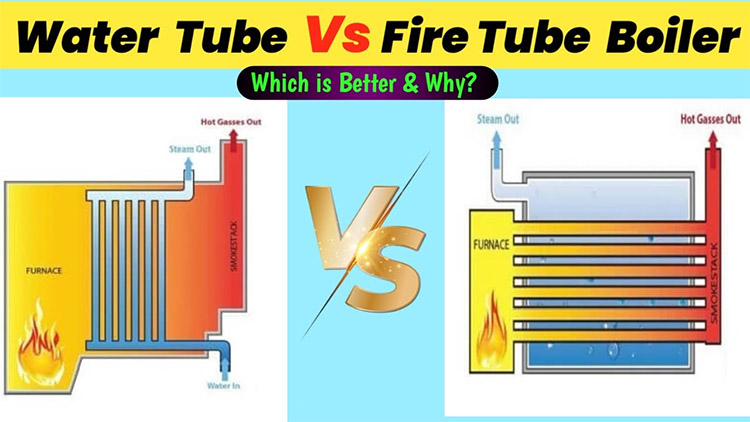
Fire Tube Boilers
In a fire tube boiler, hot combustion gases are passed through tubes that run through a sealed vessel filled with water.
This design allows the heat from the combustion gases to be efficiently transferred to the water in the vessel, which in turn produces steam. Firetube boilers are commonly used in various processes and heating applications, and are more common in small factories or places with relatively small demand for steam due to their relatively simple structure and ease of operation.
Water Tube Boilers
Water tube boilers work in a different way, with water being transported under pressure into boiler tubes surrounded by hot combustion gases. This type of boiler system is commonly found in large pharmaceutical plants, petrochemical plants, and large manufacturing plants, as well as on college campuses and government buildings.
It is capable of accommodating large-scale steam requirements and offers significant advantages in terms of thermal efficiency and operational stability.
Circulating Fluidized Bed Boiler
Circulating fluidized bed boilers employ a special combustion technology that utilizes a layer of solid particles to complete the combustion process. Within the circulating fluidized bed, the bed of solid particles is kept in circulation by the flow of gas or liquid.
Fuel is mixed with the solid particles in the bed and burned to produce high temperature gases while transferring heat to the water in the boiler. This design offers excellent combustion and heat transfer efficiencies and can accommodate a wide range of different fuel types, providing outstanding performance in terms of energy utilization and environmental protection.
Waste Heat Boilers
Waste heat boilers, on the other hand, utilize waste heat from industrial processes to create steam. In many industrial processes, a large amount of thermal energy is emitted into the atmosphere in the form of waste heat. Waste heat boilers convert this waste heat into steam energy by recovering and utilizing it.
This type of boiler is of great significance in improving energy utilization efficiency and reducing environmental pollution, and is especially widely used in some high energy consumption industries.
The working principle of steam boiler (step-by-step analysis)
Fuel Combustion and Heat Release
Industrial steam boilers can use a variety of fuels, commonly including coal, natural gas, fuel oil and so on. The fuel is ignited in the furnace chamber, triggering a violent combustion reaction that produces a high-temperature flame. During this process, the chemical energy in the fuel is released and converted into heat.
At the same time, the combustion process produces flue gas and exhaust gases, which exit the boiler through the flue.
Water Heating and Steam Conversion
The heat energy released by combustion is transferred through the walls of the furnace to the surrounding tube bundles or directly to the boiler drum. The interior of the potbelly is filled with water, and the heat is absorbed by the water during the transfer process, resulting in a gradual increase in the temperature of the water. As the temperature continues to rise, the water begins to undergo a change of state and is gradually converted to steam.
Collection and Distribution of Steam
As the water continues to heat up, the resulting steam gradually accumulates inside the cylinder. When the steam reaches the desired pressure and temperature, it is collected in a steam container located at the top of the boiler. The steam container acts as a “steam warehouse”, storing the steam temporarily.
The steam is then transported through the piping system to where it is needed, such as mechanical equipment, heating systems, or other industrial production processes, to provide power support for a variety of equipment and processes.
Flue Gas Emissions
During fuel combustion and heat release, large quantities of flue and exhaust gases are produced.
These gases need to exit the boiler through the flue to maintain the combustion process. The flue is a system of passages that directs the flow of gases and discharges the flue gases into the atmosphere. In order to reduce the emission of pollutants from the exhaust gases, the flue is usually fitted with some purification equipment, such as flue gas purifiers, to treat the exhaust gases and reduce their impact on the environment.
Fuel and Combustion Processes in Industrial Boilers
Industrial boilers are capable of converting fuel into heat, and the key to this process is the precise mixing of fuel and air to achieve controlled combustion. Different types of fuels bring variety to boiler applications. Common fuels include natural gas, oil, coal and biomass.
Each fuel has unique properties that affect the dynamic process of combustion, the rate of heat production, and the emission characteristics.
Natural Gas
Known for its clean-burning properties, natural gas is one of the most common fuels used in boilers due to its wide availability and high efficiency. During combustion, natural gas reacts more fully with oxygen and produces fewer pollutants, making it relatively environmentally friendly.
Fuel Oil
Although not as commonly used as natural gas, fuel oil is still an important boiler fuel in areas where the natural gas infrastructure is not well developed. Different types of fuel oil vary in combustion performance and energy content to meet the needs of different users.
Coal
Coal has a high energy content and has been one of the important heating energy sources. However, the combustion process of coal produces more pollutants such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides and particulate matters, which pose certain challenges to the environment. Therefore, when using coal as a fuel, it needs to be equipped with appropriate environmental protection equipment to reduce the emission of pollutants.
Biomass
As a renewable energy source, the application of biomass in industrial boilers is gaining attention. Biomass fuels are usually derived from plant materials such as wood and straw. The use of biomass fuels not only reduces dependence on traditional fossil energy sources, but also lowers carbon emissions, which is in line with the concept of sustainable development.
Application Areas of Industrial Steam Boilers

Industrial steam boilers play an integral role in a wide range of industries, and the following are some of the main areas of application.
Food Industry
In the field of industrial baking, steam boilers provide a stable heat source for ovens to ensure that bread, cakes and other baked goods can be evenly heated to achieve the desired baking effect.
In the production of baby food, steam can be used in the steaming and sterilization of raw materials to ensure the safety and quality of food.
Textile Industry
In the textile production process, rotary dryers require a large amount of steam to remove moisture from the fabric.
The efficient heat transfer characteristics of steam can dry fabrics quickly and evenly, improving production efficiency while ensuring that the quality of the fabrics is not compromised.
Chemical Industry
In chemical production, steam is often used to heat chemical reactors to provide the right temperature conditions for chemical reactions. In addition, steam is also used to maintain a specific temperature environment during the storage of chemical products to ensure product stability.
Pharmaceutical Industry
Pharmaceutical processes are extremely demanding in terms of environmental and process conditions. Steam is widely used in the pharmaceutical manufacturing process for cooking and sterilizing raw materials, as well as drying pharmaceutical products, to ensure that the quality and safety of pharmaceutical products meet strict standards.
Cosmetic Industry
Steam is used in the production of cosmetics, such as perfumes and creams, for mixing and heating raw materials and concentrating products. Precise control of steam ensures that the quality and stability of cosmetics meets the high demands placed on them by consumers.
Stationery and Printing Industry
In the printing process, steam is needed in drying tunnels to quickly dry the paper after printing. The steady heat provided by steam enables the ink to cure quickly, improving printing efficiency while ensuring print quality and avoiding problems such as ink vignetting.
Cement Industry
Steam is used in the curing of cement in the manufacturing process of cement products. Appropriate steam temperature and humidity conditions can promote the hydration reaction of cement and improve the strength and durability of cement products.
Petroleum Industry
In the process of oil storage and transportation, some heavy oils need to be heated by steam to reduce their viscosity and facilitate storage and transportation. Steam can provide stable heat to ensure that the heavy oil maintains good fluidity at the right temperature.
Wood Industry
In wood processing, steam is used to soften wood for cutting, bending and other processing operations.
In addition, steam can play an important role in the drying process of wood. By controlling the temperature and humidity of the steam, rapid and uniform drying of wood can be realized and the quality of wood can be improved.
Hospital and Hotel Industry
In hospital and hotel laundries, steam is used to heat washing machines, which improves the effectiveness of the wash while sterilizing the clothing. In kitchens, steam is used to steam food, heat dishes, etc. to meet the needs of daily operations.
Automotive and Surface Treatment Industries
In automotive manufacturing and metal finishing, steam is often used in the final metal finishing process.
Steam removes oil and impurities from metal surfaces, and through the oxidizing effect of steam, a protective film is formed on the metal surface, improving its corrosion resistance and aesthetics.
Conclusion
Industrial boilers provide indispensable power support for production operations in many industries by converting fuel into steam through a series of complex and orderly steps. From the combustion of fuel to the generation, collection and distribution of steam to the treatment of exhaust gases, each of these steps is closely interconnected and together form the basis for the efficient operation of an industrial boiler.
Different types of industrial boilers are suitable for different scenarios and needs, while the diversified fuel options further expand the scope of industrial boiler applications. In the future, with the continuous progress of science and technology, industrial boilers will move towards a more efficient, environmentally friendly direction, continue to play an important role in various industries. If you have other questions about industrial boilers, please contact us to continue exploring related knowledge.