In modern industrial production, a stable and efficient heat supply is the basis for the smooth running of many production processes. Whether it is the manufacturing process, or chemical reactions in the chemical industry, or space heating in large buildings, can not be separated from a reliable heat source. If there is a problem with the heat source supply, it will be followed by a series of difficult problems such as production stagnation, schedule delays and product quality fluctuations. The industrial boiler, as the core equipment that can stably provide a large amount of heat, has undoubtedly become the “energy heart” of many industrial fields. This article will focus on the types of industrial boilers, working principle, application scenarios and other aspects of in-depth discussion, for you to open the mystery of the industrial boiler.
Basic Definition of an Industrial Boiler
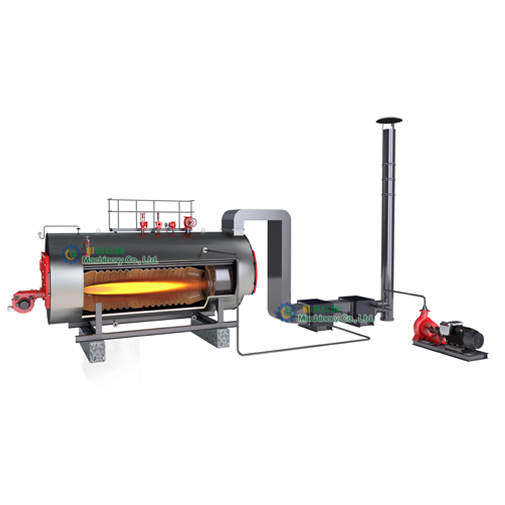

An industrial boiler is a closed pressure vessel whose core function is to convert water into steam or hot water heated to a certain temperature by applying energy to the water. In this process, natural gas, coal, oil, and electricity are usually used as energy sources. The steam or hot water produced by these will be used in a wide range of industrial applications such as manufacturing, power generation, chemicals, and many others.
Understanding the basic definition of an industrial boiler is crucial for businesses. It is not only the basis for recognizing how industrial boilers can help companies achieve cost control and improve energy efficiency, but also the key to guaranteeing the stability of their production operations. A clear grasp of the principles and characteristics of industrial boilers, companies can better choose the right equipment according to their own needs, so as to take advantage of the fierce competition in the market.
The Main Types Of Industrial Boilers
There are many different types of industrial boilers, and each type has its own unique performance and application scenarios. The following is a detailed description of the main types of industrial boilers from multiple dimensions.
Classification By Structure
Water-Tube Boiler
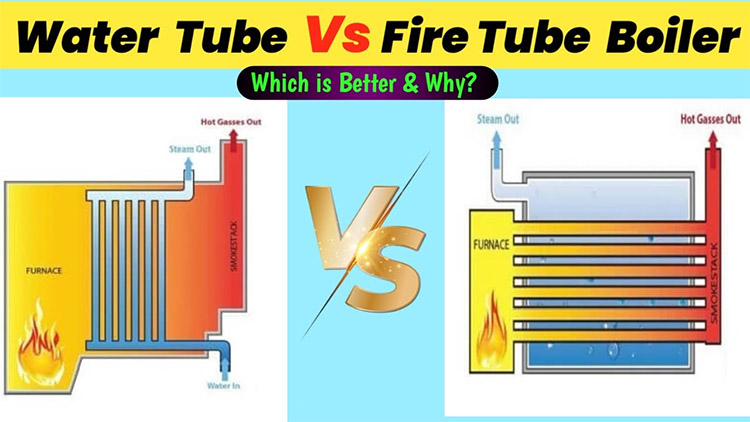
Features: In the working process of water-tube boiler, water flows inside the tubes, while high-temperature flue gas heats it outside the tubes. This structural design makes heat transfer more efficient.
Advantage: With high thermal efficiency, as well as strong pressure-bearing capacity, it can meet the demand for large-capacity steam.
Applications: Commonly used in large power plants, heavy industry, and other areas where there is a high demand for steam and high pressure capacity of equipment.
Common types: including D-type, O-type, A-type arrangement of the boiler, etc., different forms of arrangement for different production scenarios and space requirements.
Fire-Tube Boiler
Characteristics: Contrary to water-tube boilers, in a fire-tube boiler, high-temperature flue gases flow inside the tubes and water is heated outside the tubes.
Advantages: Relatively simple structure, fast startup, and easier post maintenance.
Application: Commonly used in small and medium-sized factories as well as heating systems and other scenarios that require relatively low equipment size and complexity.
Common types: including vertical fire tube boilers, horizontal shell boilers (such as Lancashire boilers), etc., suitable for different installation space and use requirements.
Smoke and Water Tube Boiler (Hybrid Boiler)
Characteristics: Ingenious combination of the structural characteristics of water tubes and fire tubes, which enables the flue gases to flush the heating surface several times, making full use of the heat.
Advantage: Compact and highly efficient equipment that can better meet the needs of medium loads.
Classification by Fuel / Energy Source
Industrial Gas (Oil-fired) Boilers
Industrial gas (oil-fired) boilers use natural gas or oil as fuel. These boilers are widely used in the U.S. for a number of reasons. Gas boilers obtain their natural gas from underground gas lines, or in rural areas where there are no natural gas mains, large propane tanks placed outside are used as the gas source. It is characterized by high energy efficiency, compact size, economic operating costs and easy maintenance, which can quickly meet the heat demand of enterprises and effectively control costs in daily use.
Solid Fuel Industrial Boilers
Coal is the most commonly used fuel for solid fuel industrial boilers, although boilers fueled by gasoline or other petroleum-based fluids are also common. The advantage of these boilers is that they can quickly reach the required temperature for production, generating heat efficiently while ensuring that the coolant reaches the desired temperature. However, the drawbacks are more obvious: the equipment is often bulky and large amounts of fuel need to be stocked in order to maintain efficient operation, which increases the site occupancy and O&M costs of the organization to a certain extent.
Industrial Electric Boilers
The industrial electric boiler is completely free from dependence on fossil fuels and utilizes electricity to achieve the water heating process. It does not produce exhaust emissions, operates quietly and takes up little space, making it an extremely environmentally friendly thermal energy device. Due to the use of electricity for heating, the heating process is clean and safe, but it requires high water quality. Usually, electric boilers are suitable for small-scale heating needs in commercial premises or homes, and are gradually being used in industrial fields in areas with strict environmental requirements and sufficient power resources.
Industrial Biomass Boiler
Industrial biomass boilers use organic materials such as wood and agricultural waste as fuel. Although the combustion process will also produce a certain amount of pollution, but compared to fossil fuel boilers, it is much less harmful to the environment. This is because the carbon burned in biomass fuels is part of the natural carbon cycle, while the carbon released from fossil fuel combustion disrupts the original carbon balance. In some areas with abundant agricultural resources, biomass boilers not only realize the utilization of waste, but also provide renewable energy for industrial production.
Industrial Heat Recovery Boilers (e.g. Condensing Boilers)
Taking the condensing boilers commonly used in the paper industry as an example, industrial heat recovery boilers are capable of recovering the energy contained in the waste heat generated during the production process, such as steam, hot flue gases and wastewater, and reusing it as fuel. In a condensing boiler, the flue gas passes through a heat exchanger before being discharged, and the heat exchanger extracts the latent heat released from the condensation of water vapor in the flue gas and reuses it for the heating process. This design greatly improves energy efficiency and reduces energy waste, making it a highly sustainable type of industrial boiler.
Classification By Working Pressure
Low pressure boiler: working pressure ≤ 2.5 MPa, commonly used in heating, food processing and other areas that do not require high pressure.
Medium Pressure Boiler: Pressure ranges from 2.5~6.0 MPa, mainly used to provide steam supply for medium-sized industries.
High-pressure boilers: Pressure ≥ 6.0 MPa, mostly used in thermal power plants and other scenarios with high steam pressure requirements.
Supercritical / Ultra-supercritical Boilers: Pressure exceeding the critical point (22.1 MPa), with extremely high thermal efficiency, commonly used in large power generation units.
Categorized By Circulation Method
Natural circulation oiler: Natural circulation is formed by the density difference between water and steam, which is simple in structure and reliable in operation, and is suitable for many conventional industrial scenarios.
Forced circulation boiler: With the help of circulating pump to drive the water flow, it can adapt to the needs of high-pressure system to ensure the stability and efficiency of water circulation.
DC boilers: Without a steam jacket, water is converted to steam in a single pass through the heating surface, compact structure, especially suitable for supercritical pressure operating environment.
Classification by Application
Industrial Steam Boilers
Industrial steam boilers heat water through a heat exchanger, and the heated water is converted into steam, which is then transported to the piping system connected to the radiators. During its operation, pressure and gravity are skillfully utilized to transport the high-temperature steam to the radiators, where the steam condenses into water after releasing heat and then returns to the boiler to be reheated, and so on and so forth, continuing to provide a stable steam heat source for industrial production. This type of boiler is widely used in textile printing and dyeing, food processing, and other industries with a large demand for steam.
Industrial Hot Water Boiler
The working principle of industrial hot water boiler mainly depends on the temperature, volume and pressure changes of water. The water is pumped through the entire system network. When the water is heated to a set temperature, it expands in volume due to the principle of thermal expansion and contraction, and is then transported to the radiators, which emit the heat into the indoor space. The cooled water is then returned to the boiler for re-heating by gravity or circulation pump, thus realizing the circular supply of hot water. It is often seen in centralized heating systems, hot water supply in hotels and other scenes.
Industrial Thermal Oil Boiler
Industrial thermal oil boiler adopts thermal oil as the heat transfer medium, replacing the traditional water. This design has significant advantages. Heat transfer oil does not evaporate like water, so it does not subject the system to excessive pressure, and it also effectively avoids corrosion and scale formation on the equipment. During operation, the gas or crude oil required for combustion is heated by the heat transfer oil, which greatly reduces the risk of explosion compared to steam boilers. In the chemical and plastics processing industries, heat transfer oil boilers have become the ideal heat supply equipment due to their stable heat transfer performance and safety.
Hot Air Boiler
Direct heating of air, commonly used in drying, drying and other production processes that require hot air.
Other Special Types
Fluidized bed boiler: fuel is combusted in the fluidized state, which is able to adapt to a variety of fuels such as low-quality coal, biomass and other fuels, and is less polluting, and has a unique advantage in the comprehensive utilization of energy.
Condensing boiler: through the recovery of latent heat in the flue gas, the thermal efficiency can be as high as 95% or more, is a representative of energy-saving and environmentally friendly boilers, which are widely used in the current focus on energy saving and environmental protection.
Working Principle of Industrial Boiler

The operation of industrial boiler is based on the principles of heat transfer and fluid dynamics, which mainly includes the following key links.
Fuel Combustion
Whether solid, liquid or gaseous fuel, a violent combustion reaction occurs in the combustion chamber. During this process, the chemical energy in the fuel is released and converted into a large amount of heat energy, providing the energy basis for subsequent heat transfer.
Heat Transfer
The hot gases or flames produced by combustion transfer heat to the water or heat transfer fluid inside the boiler. Through components such as heat exchangers, heat is transferred from the high-temperature combustion products to the low-temperature water or heat-conducting fluid, realizing the transfer of energy.
Steam Generation
When water is heated to the boiling point, vaporization occurs and steam is produced. This steam is then piped to various industrial processes for heating, generating electricity or providing mechanical power.
Control System
To ensure safe and efficient operation of industrial boilers, modern industrial boilers are equipped with an advanced control system. The system is able to monitor and adjust the supply of fuel and air, combustion rate and steam pressure and other parameters in real time, and once an abnormal situation occurs, it will immediately take appropriate measures to ensure the stable operation of the boiler.
The Main Components Of Industrial Boilers
Industrial boilers, although complex, are mainly composed of the following key components.
Burner
The role of the burner is to provide a source of heat for the boiler, it is through precise control of the mixing ratio of fuel and air, so that the fuel is fully combusted to release the maximum heat energy.
Combustion Chamber
The combustion chamber is the place where the fuel is burned, which should not only be able to accommodate the combustion process of the fuel, but also ensure the stability and safety of the combustion process and prevent heat leakage and flame outflow.
Heat Exchanger
Heat exchanger is the core component to realize heat transfer, which can efficiently transfer the heat generated by combustion to the medium inside the boiler and improve the efficiency of energy utilization.
Tanks / Water Packages
Tanks or water packages are mainly used to store water and steam, and to separate steam and water to ensure that the output steam is of high quality.
Control and Safety Valves
Control and safety valves are important devices for the safe operation of boilers. The control system regulates the operating parameters of the boiler, while the safety valve automatically opens when the pressure exceeds the set value, releasing the pressure and preventing the boiler from exploding and other dangerous accidents.
Exhaust Chimney
The function of the exhaust chimney is to safely discharge the exhaust gases produced by combustion into the atmosphere, and at the same time, through reasonable design, ensure that the process of exhaust gas discharge will not cause too much pollution to the surrounding environment.
Wide Application of Industrial Boilers
Because of their ability to produce steam and hot water, industrial boilers have an indispensable place in many industries.
Power Generation
In the power generation sector, water-tube boilers are commonly used in power plants due to their ability to generate steam at high temperatures and pressures. The steam generated drives a turbine, which in turn drives a generator to produce electricity, providing a constant source of power for society.
Food Industry
In food processing, high hygiene standards are required for steam. Steam from industrial boilers is used in the cooking, sterilization and processing of food to ensure quality and safety.
Oil & Gas Industry
In refineries and petrochemical plants, industrial boilers are used in the processing and separation of petroleum and chemical raw materials. Steam, as an important heat source, plays a key role in operations such as heating, evaporation and transportation of materials, and requires boilers to operate stably and efficiently for long periods of time.
Chemical Industry
There are a large number of chemical reactions and material heating processes in chemical production, which require industrial boilers capable of generating high-temperature and high-pressure steam to meet the production requirements and ensure the smooth production of various chemical products.
Textile Industry
In the textile printing and dyeing process, steam is used to regulate the temperature of fibers and fabrics, and is also indispensable in dyeing, washing and other processes. The use of steam from industrial boilers can effectively improve the quality of textiles and shorten production cycles.
Pharmaceutical Industry
In the pharmaceutical industry, the purity of steam is required to be extremely high. The high purity steam produced by industrial boilers is used to sterilize pharmaceutical equipment and raw materials, as well as to control the temperature of the pharmaceutical production process, which is directly related to the quality and safety of pharmaceutical products.
Paper Industry
In the paper making process, steam generated by industrial boilers is used to evaporate the water in the pulp, as well as to regulate the temperature in different production stages, helping the paper to dry faster and more uniformly, and improving the quality and efficiency of paper production.
Centralized Heating System
Hot water boilers are widely used in the centralized heating system of large buildings, residential communities, hospitals, hotels and other places to provide people with a warm and comfortable living and working environment.
Industrial Car Wash
In the field of industrial car wash, the steam produced by industrial boilers can efficiently clean and disinfect vehicles, large machinery and equipment, and various surfaces to meet the high standard requirements of industrial cleaning.
Factors in Selecting an Industrial Boiler
Selecting the right industrial boiler requires a number of factors to be considered to ensure that the equipment meets the actual needs of the business.
Capacity / Steam Demand
Enterprises should first accurately calculate the required steam output or heating capacity based on their production process and equipment configuration. If the boiler capacity chosen is too large, it will lead to energy waste and increased operating costs; if the capacity is too small, it will not be able to meet the production demand. At the same time, the future development plan of the enterprise should also be taken into full consideration, leaving a certain amount of space for capacity expansion.
Fuel type
Different fuels have different availability, costs and environmental impacts. Companies need to choose the most appropriate fuel type, taking into account local fuel availability, cost budgets and environmental requirements. For example, in areas where natural gas is in plentiful supply, a gas boiler may be the more economical and environmentally friendly choice, while in areas where coal is plentiful, a solid fuel boiler may have a cost advantage.
Physical Size Limitations
Companies need to make a detailed assessment of the available space in the boiler room, including ceiling height, floor area, and operating space required for equipment maintenance. If space is limited, a compact boiler model will need to be selected to ensure that the equipment can be installed and operated smoothly.
Budget
In addition to considering the purchase cost of the boiler, companies should include long-term operating costs in their budgets, including fuel costs, equipment maintenance costs, and operator labor costs. Although the initial investment in an energy efficient boiler is higher, it can save the enterprise a lot of operating costs in the long run.
Efficiency Requirements
Choosing an industrial boiler with high thermal efficiency not only reduces fuel consumption and operating costs, but also lowers emissions and meets environmental requirements. Enterprises should choose boiler equipment that meets efficiency requirements according to their own energy consumption targets and environmental policies.
Installation and Maintenance of Industrial Boilers
Installation Process
The installation of industrial boilers requires professional technology and strict specifications. Before installation, a comprehensive assessment of the installation site should be carried out to ensure that the site conditions meet the installation requirements of the boiler. During the installation process, it is important to strictly adhere to the relevant regulatory standards, such as the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code. At the same time, the boiler must be properly integrated with the company's existing infrastructure for optimal operation.
Maintenance Practices
Regular inspection, cleaning and maintenance of industrial boilers is essential to ensure proper operation and long service life. This includes cleaning of components such as burners and heat exchangers, calibration of control systems, and testing of overall equipment performance. Preventive maintenance measures enable potential problems to be detected and resolved in a timely manner to avoid equipment failures from affecting production.
Safety Protocols
In order to ensure the safety of operators and the stable operation of the equipment, enterprises need to formulate perfect safety operation procedures and emergency plans. Conduct professional training for boiler operators to familiarize them with the operating procedures and safety precautions of the equipment. At the same time, regular safety drills are organized to improve the ability to deal with unexpected accidents and ensure the safety of enterprise production.
As an important heat supply equipment in industrial production, industrial boilers are of various types, each with its own characteristics and applicable scenarios. Enterprises in the selection and use of industrial boilers, you need to fully understand its performance and characteristics, take into account a variety of factors, and do a good job of installation and maintenance work, in order to achieve efficient, safe and sustainable production and operation.