In the industrial heat supply system, fire tube boilers have become the first choice of heat supply for many enterprises and organizations by virtue of their efficient heat transfer mechanism and economical operation cost. This article will analyze the core components of the fire tube boiler, a comprehensive introduction to its type, maintenance points and application scenarios, for readers to build a systematic and complete knowledge system.
The basic knowledge of the fire tube boiler
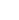
The fire tube boiler uses hot gas as the medium of heat transfer. When working, the high temperature gas flows in the tubes of the water-filled drum container, and through heat conduction, convection and radiation, the heat is efficiently transferred to the water in the container, which in turn generates steam. This kind of boiler has the remarkable features of simple design, convenient operation, low purchase cost, etc. It can flexibly meet the heat demand of medium and low pressure, and can be customized with diversified structural forms according to the needs of different application scenarios.
In-depth analysis of core components
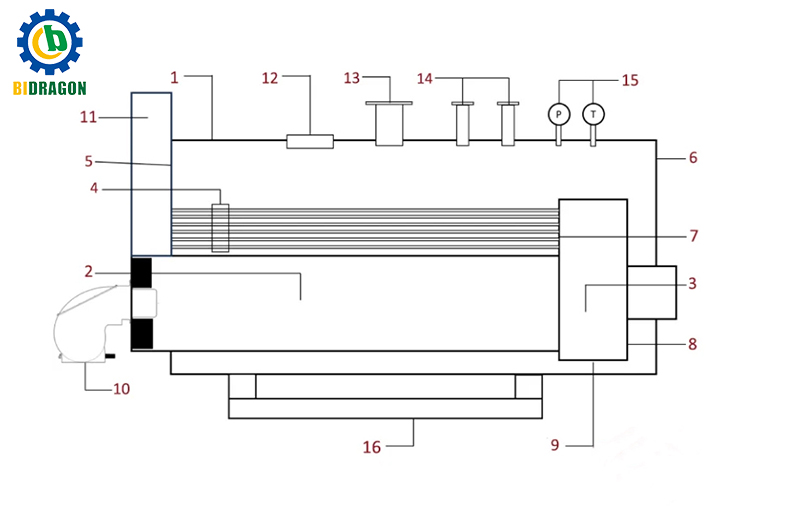
- Boiler Shell
Boiler shell is the main pressure vessel in the fire-tube boiler subjected to high temperature and high pressure, and filled with water or heat-conducting oil inside, which is the main space for heat exchange process. The boiler shell is usually made of high-strength carbon steel or alloy steel materials, with advanced welding technology, to ensure long-term pressure without deformation, is to ensure the safe operation of the boiler foundation.
- Combustion Chamber
Combustion Chamber is the area where the fuel is mixed with air and burned, and the heat energy released during the combustion process heats the water inside the pot shell by radiation, convection and conduction. About 40%-45% of the heat is initially transferred at this stage. Combustion chamber materials need to be resistant to high temperatures and corrosion to ensure efficient combustion and heat transfer. 3.
- Reversal Chamber
After combustion, the flue gas first enters the Reversal Chamber (also known as steering chamber), which is designed to guide the high temperature flue gas to the second flue pipe channel, and in the process continue to release some heat to the water to improve heat utilization. Combustion chamber design needs to take into account the sealing, strength and heat transfer capacity.
- Smoke Tubes
Smoke tubes are the most important heat transfer element in a fire-tube boiler. High-temperature flue gas flows at high speed in the tube, and its heat is transferred to the water through the tube wall, realizing the efficient conversion of heat energy to steam. The length, diameter and arrangement of the flue tube will directly affect the thermal efficiency and evaporation capacity of the boiler.
- Front Tube Plate
Front Tube Plate is the fixed starting end of the boiler flue pipe, which needs to have high mechanical strength and sealing performance to ensure the stable operation of the flue pipe under high temperature and high pressure.
- Rear Tube Plate
Rear Tube Plate is located at the end of the boiler, plays a role in fixing the end of the flue pipe and sealing the gas path, and works together with the Front Tube Plate to stabilize the flue pipe system.
- Reversal Chamber Tube Plate
This tube plate is located in the Reversal Chamber and is used to support and secure the second stage of the flue pipe to ensure that the flue gases can flow smoothly into the next stage of the heat exchange system.
- Outlet Flange
Outlet flange is the connecting part of the boiler for the medium or hot gas to leave the system, commonly used for connecting the pipeline, heat exchanger equipment or dust removal system, and its sealing performance must be in accordance with the boiler design pressure and temperature standards.
- Wrapper Plate
Wrapper Plate is set around the combustion chamber, responsible for guiding the flue gas back to the second course of the flue pipe, prolonging the residence time of the hot gases in the boiler, and improving the heat utilization rate. Good flow channel design is an important factor to improve the thermal efficiency of the boiler.
- Burner
Burner can realize the precise proportion and full combustion of air and fuel, and quickly convert chemical energy into heat energy. Modern burners are equipped with intelligent control modules, with automatic ignition, flame monitoring and fault self-testing functions, effectively improving combustion efficiency and operational safety.
- Stack
The chimney is the final emission path of the boiler flue gas and transports the flue gas safely to the atmosphere. Some high-efficiency stack systems are integrated with environmental protection devices such as desulfurization, denitrogenation and dust removal to meet increasingly stringent emission standards.
- Inspection Openings
The boiler shell is equipped with a number of inspection openings, which allow operators to use endoscopes or inspection tools to check internal scaling, corrosion and structural damage, and to detect hidden problems in time to ensure the safe and stable operation of the boiler.
- Safety Valves
When the pressure in the boiler exceeds the design upper limit, the safety valve will automatically open to release the pressure, preventing accidents such as equipment explosion. It is the most critical active safety line of defense in the boiler system.
- Pressure Gauge & Thermometer
These two devices monitor the pressure and temperature inside the boiler in real time, which is an important basis for the operator to judge the working condition of the boiler. Some of the systems support linkage alarm or remote monitoring to enhance the level of intelligent operation.
- Supports
The boiler support system is customized according to its operating weight and vibration characteristics to ensure that the equipment remains stable under high temperature, high pressure and constant vibration. High-end support systems are also equipped with vibration damping modules to effectively reduce operating noise and wear and tear.
- Inspection openings
In addition to the main inspection holes, but also set up part of the small inspection ports for specific areas (such as the combustion chamber or flue pipe area) of the rapid observation or probe measurements, is an important component of the auxiliary means of inspection.
- Boiler Power and Control System
modern fire tube boilers equipped with advanced control systems, pumps, burners, sensors, instruments and other integrated linkage, support for remote control, automatic operation mode and intelligent alarm analysis, greatly enhancing the level of boiler intelligence and operational efficiency
Type Division and Typical Representatives
Classification Dimensions
The type division of fire-tube boilers is mainly based on the following dimensions: according to the different locations of the hearth, it can be divided into the outer hearth type and the inner hearth type; according to the difference in the direction of the axis, there are differences between the horizontal and the vertical type; and based on the morphology characteristics of the fire tube, it covers a wide range of types, such as single tube, multiple tubes, straight tubes and curved tubes.
Mainstream Models
-Cauchlan boiler: designed with vertical structure, it is suitable for heating scenarios with low pressure (≤10.5bar) and low output (≤3500kg/h), and is commonly used in small-scale heating systems as well as in some industrial production processes with low demand for steam.
-Cornish boiler: belonging to the horizontal single flue design, capable of providing medium pressure (≤12bar), medium capacity (≤6500kg/h) steam output, in the past, it used to dominate the supply of steam power in the mining industry.
-Locomotive boiler: With a horizontal multi-tube structure and built-in hearth, it is capable of generating high-pressure (≤25bar), high-capacity (≤9,000kg/h) steam, and was the core power equipment driving train operations in the era when steam locomotives were prevalent.
-Scottish marine boiler: adopting horizontal multi-furnace structure, it can realize high-pressure (≤30bar), high-capacity (≤27000kg/h) steam supply, and it is the key equipment in the power system of the ship, and it is widely used in the power, heating and other heat demand scenarios of all kinds of ships.
Full-cycle Maintenance Strategy
External Inspection Points
In the course of daily operation, maintenance personnel need to carefully verify the boiler's operating certificate to ensure that it matches the boiler's actual parameters and operating requirements; carefully compare the parameters of the safety valve to ensure that it is within the normal operating range; conduct strict testing of the water level control device to ensure that the water level is stable and safe; comprehensively inspect the piping system for any leakage conditions Regularly calibrate the accuracy of instruments such as pressure gauges and thermometers to ensure the accuracy of their data, so as to ensure that the whole system can operate in a compliant and safe manner.
Internal overhaul specification
Before carrying out internal overhaul, it is necessary to shut down and wait for the boiler to cool down to a safe temperature. At the same time, the oxygen content inside the boiler should be tested, and only after the oxygen content meets the standard and it is confirmed that there is no flammable, explosive or harmful gas, the maintenance personnel can enter. After entering the boiler, focus on checking the scale deposition, whether there is corrosion of the tube wall, whether the refractory bricks are loose and other issues, in particular, the weld of the tube plate and the integrity of the supporting structure should be carefully examined, and potential safety hazards should be found and repaired in a timely manner.
Core Competitive Advantages
Compared with other types of boilers, fire tube boilers have significant competitive advantages. Its compact design can accommodate a large amount of water in a limited space, increasing the heat storage capacity; dense distribution of heat transfer surface greatly improves the heat exchange efficiency, so that the heat can be more quickly and adequately transferred to the working fluid; a wide variety of configuration options to meet the differentiated needs of different users; in addition, due to its relatively simple structure, easy maintenance, long-term, operation and maintenance costs have also been significantly reduced. Reduce.
Cleaning and Maintenance Process
Preparation Stage
First, the boiler is shut down and allowed to cool naturally to a safe temperature. Subsequently, cut off the energy supply to the boiler, including electricity and fuel, effectively isolate the boiler from the entire heating system, and take necessary safety measures, such as setting up warning signs and installing guards, etc., so as to build up a safety line for the subsequent cleaning and maintenance work.
Step-by-step cleaning
First, clean the external surface of the boiler to remove the attached dust, oil and other impurities. Then, open the front and back doors of the boiler, and use professional brushes, scrapers or pneumatic tools to carefully remove deposits such as ash and scale in the flue pipe and combustion chamber. During the cleaning process, special attention should be paid to avoid damage to the surface of the flue tube. After the cleaning is completed, use vacuum equipment to thoroughly clean the loose debris and residues in the combustion chamber and on the surface of the flue pipe. For severe scaling or stubborn deposits that are difficult to remove, it is necessary to formulate a suitable chemical cleaning agent in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations or industry standards, and deliver the cleaning agent into the flue pipe through a circulating pump so that it can fully dissolve and loosen the deposits. Finally, a complete rinse of the boiler interior is carried out using a high-pressure water jet to ensure that all cleaning agents, deposits and residual impurities are completely removed.
Acceptance Restart
After completion of the cleaning work, all internal components of the boiler are thoroughly inspected for any damage or wear and tear of parts caused by the cleaning process. Replace or repair any damaged parts found. When reassembling the boiler, make sure that all connections are strong, reliable and well sealed. After completing the assembly, carry out the necessary sealing test, and restart the boiler only after passing the test in accordance with the operating procedures. At the same time, establish a detailed maintenance file to record the relevant information of this cleaning and maintenance, including the cleaning time, cleaning personnel, problems found and treatment measures, etc., so as to follow up and analyze the operation status of the boiler in the future.
Diversified Application Scenarios
In the medical field, fire tube boilers are mainly used to ensure the supply of hot water to hospitals, the sterilization of medical equipment and the heating needs of wards, operating rooms and laboratories and other areas, to provide stable heat support for the normal conduct of medical work. In the food processing industry, fire tube boilers are widely used in cooking, disinfection, drying and equipment cleaning processes, and can provide economical and efficient medium and low pressure steam to meet the strict hygiene and quality requirements of food processing. In campus scenarios, fire tube boilers take into account the heating needs of the campus as well as the operation of laboratory equipment heat, its operation process is quiet, small footprint, ideal for schools, libraries and other places with high environmental requirements. In government buildings, fire tube boilers provide hot water supply for office buildings and public facilities through district heating systems, and serve as a backup heat source to meet emergency needs in case of emergency. It has the advantages of high cost-effectiveness and easy installation, meets the requirements of public budget management, and can effectively guarantee the stable operation of public facilities.
Conclusion
From the functional principle of the core components to the diverse application scenarios, the fire tube boiler fully demonstrates the perfect integration of precision engineering technology and practical value. Whether in the boiler selection process to provide users with a reference basis, or in the operation and maintenance of equipment to give professional guidance, the knowledge framework built in this paper can provide strong technical support for practitioners in related industries. If you need further technical advice or customized equipment solutions, please feel free to communicate with us.